The blockchain technology and the concept of digital assets are relatively young phenomena. And ever since the first digital currency – Bitcoin, was introduced to the world back in 2009, the Cryptocurrency market has been experiencing a rollercoaster ride.
Whilst the market uncertainty prevails and even the biggest companies occasionally find themselves at a tragic end due to misconduct or external factors, many speculate about possible repercussions a global Crypto collapse can bring upon the Cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Among the many interesting scenarios that could cause such an event, one remains quite popular and is likely the most heavily discussed:
What would happen if Bitcoin’s price dropped to zero?
A seemingly simple question, yet one that demands a thorough examination of the broader context to provide a meaningful answer. Over the years, Bitcoin has experienced several significant price crashes, yet it has consistently demonstrated resilience through notable recoveries. This chart highlights pivotal moments when Bitcoin’s price reached its lowest during market downturns and subsequently rebounded, illustrating its cyclical behavior and long-term stability within the cryptocurrency market
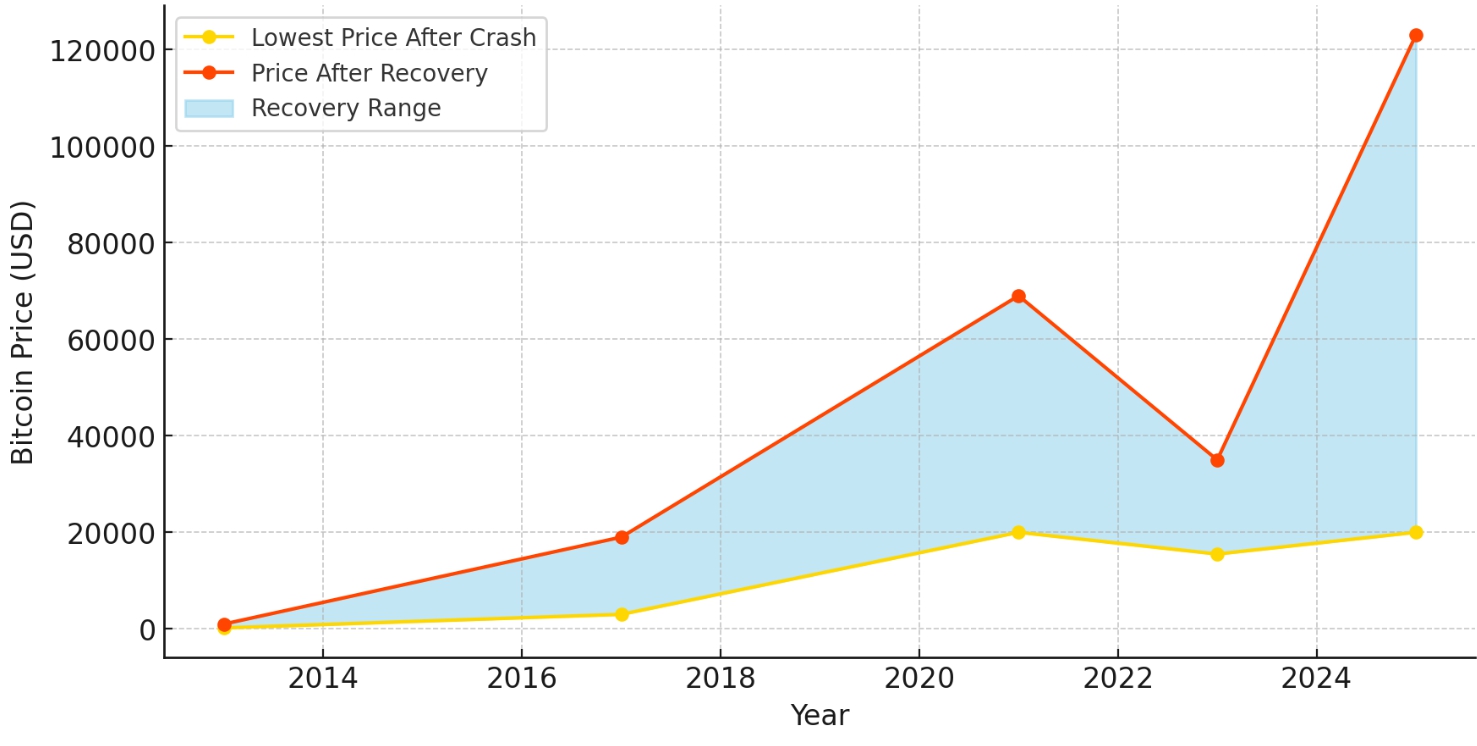
Data Points:
- 2013: Dropped from $1,000 to $200, then rebounded.
- 2017: Fell from $19,000 to $3,000, then rebounded.
- 2021: Dropped from $69,000 to ~$20,000 but stabilized
- 2025: Surged above $120,000, setting a new all-time high.
The Forces Driving Bitcoin’s Value
In order to solve this puzzle and come to a logical conclusion, it is vital to consider several factors and mechanics in motion, such as the driving force of Bitcoin and it’s value on the market.
Bitcoin is not a stablecoin, which means thats it’s value is not tied to any tangible asset, like the US dollar is backed by gold reserves.
This makes it vulnerable to significant price drops and/or any sudden upward spikes on a daily basis, just like any other Crypto asset.
In 2024, Bitcoin experienced a notable resurgence driven by the approval of multiple spot Bitcoin ETFs in the United States, which opened the door for large institutional investors to pour capital into the market. This development, combined with the anticipation and subsequent completion of the 2024 halving event, pushed Bitcoin above $70,000 for the first time since late 2021.
In 2024, Bitcoin experienced a notable resurgence driven by the approval of multiple spot Bitcoin ETFs in the United States, which opened the door for large institutional investors to pour capital into the market. This development, combined with the anticipation and subsequent completion of the 2024 halving event, pushed Bitcoin above $70,000 for the first time since late 2021.
In 2024, Bitcoin experienced a notable resurgence driven by the approval of multiple spot Bitcoin ETFs in the United States, which opened the door for large institutional investors to pour capital into the market. This development, combined with the anticipation and subsequent completion of the 2024 halving event, pushed Bitcoin above $70,000 for the first time since late 2021.
Fundamentally speaking, volatility is the core characteristic of the Crypto market making any digital asset prone to skyrocket or crash in a matter of months, days or even minutes.
And Bitcoin’s price is no exception to this rule, as it’s historical performance proved this on multiple occasions.
Throughout the recent years several factors have affected the price of Bitcoin. Such as Donald Trump’s statement back in June of 2021 that “Bitcoin is a scam”.
Or the announcement of Elon Musk – Tesla’s CEO, earlier in May that Bitcoin will no longer be accepted as a payment method for produced vehicles.
Both with a negative impact on the price by nearly 55%, settled Bitcoin from a high of $57,352.77 to a low of $31,397.31.
Yet subsequently it rose over the course of the second half of the year hitting a record high of $64,863.98 as El Salvador was the first country to embrace Bitcoin as a legal tender.
Unfortunately many regulatory changes, the 2022 Bitcoin incident when Binance froze withdrawals and the cascade collapse of FTX and other crypto exchanges all together depleted Bitcoin of it’s value, making it depreciated as much as it was back in November of 2020 at a yearly low of $16,195.59.
However, in 2025 Bitcoin not only recovered but also shattered previous records, reaching a new all-time high above $123,000 in July. This surge was fueled by unprecedented institutional adoption, geopolitical uncertainty driving investors toward decentralized assets, and major legislation in the U.S. providing clarity on crypto regulations.
Could Bitcoin’s Price Drop to Zero?
In the light of these events concerns arise. A reasonable assumption that Bitcoin could hypothetically reach the null state of it’s value is worth the thought.
Even-though such an event is very less likely to take place, there are some factors that could theoretically lead to Bitcoin price crashing to zero.
Among many, here are the most hazardous ones. Those, which can lead to severe consequences and hypothetically terminate Bitcoin as a currency with a market price:
Key Market Mechanisms Impacting Bitcoin
In contrast to the stock market, the cryptocurrency market does not have a circuit break. Which means that the trading sessions are never paused.
Such mechanics are downside accelerators when the price of a certain currency faces an extreme drop in the event of a massive sell-off.
Moreover, if a sell-off triggers panic, similar to the one that subjugated thousands during the FTX collapse, it can undermine consumer confidence.
Crypto investors may proceed with further sell-offs exponentially multiplying the disaster which might lead to a drop to zero.
However, in recent years new dynamics have emerged that can counterbalance this effect. The approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in 2024 introduced a wave of institutional capital with stronger risk management practices, which added some stability to the market. Additionally, the 2025 Bitcoin rally to an all-time high of over $123,000 highlighted how positive regulatory clarity and adoption by sovereign entities can reverse even deep negative sentiment.
External Threats to Bitcoin’s Stability
Beyond internal factors that may affect the price of Bitcoin, a number of external threats can also pose immense danger. Scalability issues are one of those.
As volume on the Bitcoin network rises with each transaction, latency increases, which in it’s turn intensifies insufficiency of processing operations.
Despite the ever growing Cryptocurrency ecosystem and more Bitcoin investors joining the community, global market competition pulls it’s share of the blanket.
Heating interest around artificial intelligence and it’s capabilities switches the focus of investors, giving them alternative purposes to consider.
Another nemesis to digital currencies are escalating implementations of strict regulatory frameworks that force investors to free cash towards other obligations.
In addition to that, the US Federal Reserve places higher interest rates thus cultivating a hostile environment that affects Crypto prices.
While Bitcoin faces theoretical risks that could drive its price to zero, there are several factors that provide significant stability to its value. This chart highlights the key elements that underpin Bitcoin’s resilience, such as its decentralized network, limited supply, and growing institutional adoption. These factors counterbalance potential market vulnerabilities, demonstrating why a complete collapse, though possible, remains highly unlikely under normal circumstances.
As technology progresses, a potential threat to Bitcoin’s stability arises from quantum computing. Quantum machines are theoretically capable of breaking the cryptographic algorithms that underpin Bitcoin’s security, such as ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm).
If quantum computing becomes advanced enough, it could allow malicious actors to forge private keys and compromise wallets. However, many experts argue that this threat remains distant, as post-quantum cryptography solutions are already in development. Developers are actively exploring ways to transition Bitcoin to quantum-resistant algorithms, ensuring its survival in the face of technological revolutions.
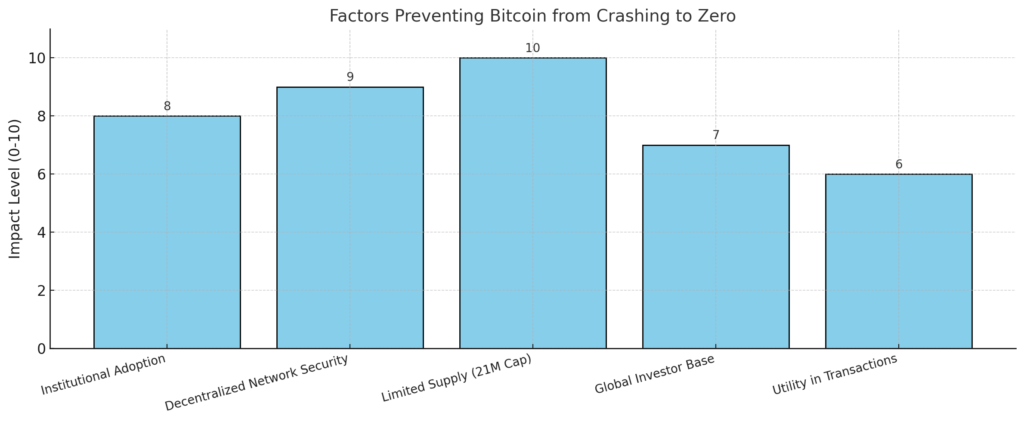
- Institutional Adoption
As institutional investors like banks, hedge funds, and publicly traded companies integrate Bitcoin into their portfolios, it reinforces trust and long-term stability. Institutional adoption adds liquidity to the market and signals confidence to smaller investors, reducing the likelihood of a complete price collapse. - Decentralized Network Security
Bitcoin’s blockchain is maintained by a global network of miners, ensuring it is nearly immune to centralized failures or attacks. This decentralization makes Bitcoin highly secure, giving users confidence in its continued functionality and preventing large-scale abandonment. - Limited Supply (21 Million Cap)
Bitcoin’s hard cap of 21 million coins creates digital scarcity, similar to precious metals like gold. This scarcity is a key driver of its value and prevents inflationary devaluation, which is common with fiat currencies. The fixed supply makes it unlikely to lose all value, even during market downturns. - Global Investor Base
Bitcoin’s adoption spans across borders, with millions of individuals, businesses, and institutions investing worldwide. This global demand ensures that Bitcoin remains valuable in diverse economic conditions, reducing the risk of a complete market collapse. - Utility in Transactions
Beyond investment, Bitcoin serves as a payment method for cross-border transactions and a hedge against inflation in some economies. Its utility creates ongoing demand, making it more than just a speculative asset and less likely to lose all value
The Ripple Effect of a Bitcoin Crash
If Bitcoin lost all of its value and utility at once, the potential impact would be immense and most definitely lead to massive financial losses among individual investors, various companies and on the global cryptocurrency market.
A hypothetical ban on all operations with the mastodon among digital currencies would first affect Bitcoin miners, who rely on it as their main source of income.
Immediate dismissal from Bitcoin mining, would force almost a million miners to search for alternative sources to make a living.
Along with them, all major stakeholders like lending or swapping companies would face the harsh reality of shutting down and filling bankruptcy reports.
And lastly but not the least, would bring down a destructive wave upon other cryptocurrencies due to the nature of their dependency on Bitcoin.
How Bitcoin’s Fall Could Shake Crypto Markets
Bitcoin has long held the position of a market leader, often dictating the overall sentiment and direction of the cryptocurrency ecosystem. If Bitcoin were to experience a catastrophic collapse, the ripple effect on other digital assets would likely be immediate and severe.
Most altcoins, including major players like Ethereum, Binance Coin, and Solana, have historically mirrored Bitcoin’s price movements. A sharp decline in Bitcoin’s value would trigger panic selling across the market, leading to significant losses in altcoin portfolios.
Furthermore, projects heavily reliant on Bitcoin’s infrastructure—such as wrapped tokens, Bitcoin-backed stablecoins, and cross-chain bridges—would face technical and liquidity crises. The entire DeFi sector, which uses Bitcoin as collateral in many protocols, could experience widespread liquidations and insolvencies.
While some argue that Ethereum and other blockchains have enough independent utility to weather such a storm, the reality is that Bitcoin’s collapse would fundamentally shake confidence in the viability of cryptocurrencies as a whole, potentially ushering in a prolonged “crypto winter” unlike anything seen before.
Economic Impact of a Bitcoin Collapse
Prolonged consequences of the crash may cause significant changes in the economic model of the blockchain technologies, related projects and in the approach of delivering fintech innovations to the world.
Perchance the digital assets will no longer be the centre piece of many former crypto fintech companies that will shift their focus to providing products and solutions to the global market to attract traditional investments.
Can Bitcoin Really Hit Zero Value?
The decentralised infrastructure and the robust architecture of the blockchain make it nearly impossible to put it at an absolute halt.
A complete failure of the thriving system would require an unrecoverable loss of interest to over a 100,000 active nodes within the Bitcoin network.
Besides the obvious technical advantages, the size of the community surrounding the first Cryptocurrency backs the claims of it’s sustainability in the face of a potential crash.
The support of crypto whales and thousands of individuals natively strengthens the asset’s value. Moreover, their contribution to it’s resilience multiplies the community and raises global awareness.
Strategies for Surviving a Bitcoin Downturn
In the real world, the Cryptocurrency market remains unstable and prone to frequent fluctuations.
And despite a proven track record of Bitcoin historically performing well against the odds of internal and external factors, risk management lies in the core of any investment strategy.
Navigating and trading a potential steep decline in Bitcoin’s price requires much more knowledge than a raw theoretical base and absorbed speculations.
Selling or buying Bitcoin during a turbulent time should always be conducted in accordance with best practises, accompanied by a selection of proper analytical tools.
Mastering Risk Management in Crypto
As appealing Bitcoin may seem to invest in, a good to go practise to mitigate the risk associated with a single asset is diversification. Spreading the risk helps offset losses by balancing them out with profits made in a different investment.
Another great way to protect an investment from losses is the utilisation of Stop Loss orders.
By placing orders that automatically trigger when the price reaches a certain threshold, any potential losses can be easily limited to an acceptable level.
The Psychology of Investing During a Crash
Following a short-term trading strategy can bring various benefits, yet result in unfavourable outcomes in the long-term in the event of an unexpected situation.
Because of this, its vital to remain unbiased in choosing a strategy to execute. Adapting properly to the current conditions offered by the market could bring more advantages and profit opportunities.
Conclusion
While the prospect of Bitcoin crashing to zero is minimal considering all factors that can influence this cause within a hypothetical theory, trading or investing in the first Cryptocurrency on a daily basis may become a difficult task.
Exercising proper risk management both in the short or long terms can ensure a balanced strategy regardless of the current or predicted price trends.
Can Bitcoin prices go to zero?
While it’s theoretically possible for Bitcoin prices to drop to zero, the likelihood is extremely low. Bitcoin has a decentralized network of miners, developers, and investors that provide intrinsic value. Additionally, institutional adoption and utility as a store of value make a complete collapse improbable unless global trust in cryptocurrencies is entirely eroded.
Is it possible for Bitcoin to collapse?
Bitcoin could face significant price declines due to regulatory crackdowns, market sentiment shifts, or technological vulnerabilities. However, its collapse is unlikely as it has weathered multiple market crashes and continues to attract investment due to its scarcity and decentralized nature
How high will Bitcoin go in 2025?
Predictions for Bitcoin’s price in 2025 vary widely, with some analysts forecasting values between $100,000 and $500,000. Factors like halving events, institutional adoption, and global economic conditions will play a key role in determining its price trajectory
Will crypto ever go back up?
Cryptocurrency markets are cyclical, and periods of downturn are often followed by growth phases. Historically, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have rebounded after market corrections due to increasing adoption, technological advancements, and a growing user base.
What causes Bitcoin prices to drop suddenly?
Bitcoin prices can drop due to a variety of reasons, including:
Negative regulatory news.
Large-scale sell-offs by institutional investors or whales.
Market manipulation.
Security breaches on major exchanges.
Changes in macroeconomic factors like inflation or interest rates
Why does Bitcoin's price fluctuate so much?
Bitcoin’s price volatility is driven by:
Limited supply and high demand.
Speculative trading and market sentiment.
Lack of regulation in some markets.
Global economic and political events.
Technology updates and ecosystem changes
What happens to Bitcoin after all 21 million are mined?
Once all 21 million Bitcoins are mined (around 2140), miners will earn rewards solely from transaction fees rather than block rewards. This could impact mining profitability but ensures the network remains operational
Can Bitcoin survive without miners?
No, Bitcoin relies on miners to validate transactions and secure the blockchain. Miners play a critical role in maintaining the network’s integrity and decentralization
What are the risks of investing in Bitcoin?
Some risks of Bitcoin investment include:
High price volatility.
Regulatory changes or bans.
Cybersecurity risks (hacks, phishing, etc.).
Loss of private keys leading to lost funds.
Market manipulation by large players.
The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended as personal investment advice and does not constitute a solicitation or invitation to engage in any financial transactions, investments, or related activities. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
The financial products offered by the Company are complex and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. These products may not be suitable for all investors. Before engaging, you should consider whether you understand how these leveraged products work and whether you can afford the high risk of losing your money.
The Company does not accept clients from the Restricted Jurisdictions as indicated in our website/ T&C. Some services or products may not be available in your jurisdiction.
The applicable legal entity and its respective products and services depend on the client’s country of residence and the entity with which the client has established a contractual relationship during registration.




