CFDs empower traders to benefit from price shifts without needing to own the asset in question. By not possessing the underlying asset, CFD traders can sidestep some of the limitations and expenses associated with conventional trading.
Trading CFDs (contracts for difference) is a way of speculating on financial markets that doesn’t require the buying and selling of any underlying assets. When traders agree to trade CFDs, they enter into a contract with the broker. The trader, or “buyer,” and the broker, or “seller,” agree to a contract in which they speculate on the price of an asset in market conditions. While the trader speculates on financial products, the key distinction between CFDs and regular trading should be noted.
What is CFD trading?
CFD trading is described as “the buying and selling of CFDs,” with “CFD” denoting “contract for difference.” CFDs are a type of derivative since they allow you to speculate on financial markets like Stocks, currencies, Indexes, and Commodities without having to hold the underlying assets.
Instead, when you trade a CFD, you’re agreeing to exchange the difference in an asset’s price between when the contract is opened and when it’s closed. One of the key advantages of CFD trading is that you can bet on price fluctuations in either direction, with the amount of profit or loss determined by how accurate your forecast is.
Main features and uses of Contracts for Difference
Contracts for difference (CFDs) trading is a type of financial market speculation that does not need the purchase or sale of any underlying assets. Learn everything there is to know about CFD trading, including what it is and how it works, as well as short trades, leverage, and hedging.
The sections that follow describe some of the most important characteristics and applications of contracts for difference:
- Short and long trading
- Leverage
- Margin
- Hedging
Short and long CFD trading
The ability to trade long and short on the markets is one of the most appealing features of a CFD trading platform. When it comes to buying and selling, you can only make money if prices are growing.
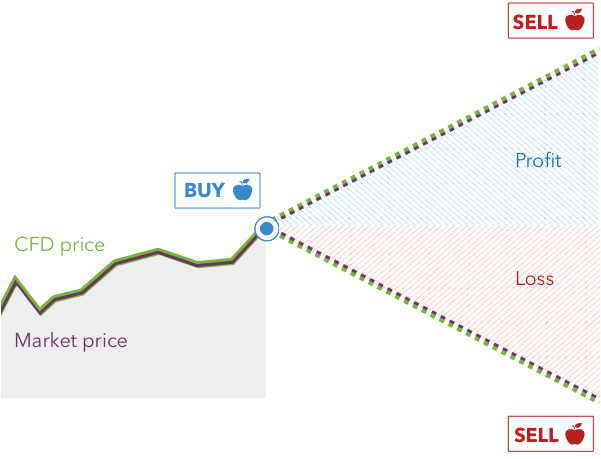
Traders may earn from both rising and falling markets by using long and short positions, and they can always be ready for an opportunity no matter which way the market goes next.
Short and long trades can be made at the same time, with distinct targets and prices. Hedge positions and other complex trading tactics are also possible.
When markets are falling, a trader should establish a short position and close it when the price has fallen sufficiently to support or earn the required profit.
When markets are rising, a trader will open a long position in the hopes of seeing the price rise. The trade can be closed and profit booked if it reaches the intended resistance or profit.
If a trader makes a mistake and their position goes against them, a stop loss will be triggered, or traders can manually closeout at a loss.
The win-to-loss ratio and total profit or loss will eventually determine whether or not a trader is profitable.
Leverage in CFD trading explained
Leverage is a strategy used by expert traders to increase the return on their capital by increasing price movements by a particular factor.
A 0.01 BTC trade with 100x leverage, for example, would result in a 1 BTC position. A $100 trade multiplied by 100 would result in a $10,000 trade in US dollars.
On more stable Forex currencies, leverage ranges from 3x to 1000x on CFDs. This is how dealers wring more profit out of a normally stable market. However, because of the extreme volatility of Cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, it is more typically traded at 100x.
The main reason why any trader would want to use leverage is to increase their profits. Leverage boosts the stakes, making trading a high-risk, high-reward proposition.
The main reason why any trader would want to use leverage is to increase their profits.
When $10,000 becomes a $1 million investment, you can appreciate the potential of 100x leverage. This type of intraday movement is not uncommon in the Cryptocurrency market.
However, the Cryptocurrency markets tend to be much more volatile then Forex or Commodities markets. Proper risk management and use of stop loss and take profit orders is key to protecting you from undesired outcomes, if the market shifts in the opposite direction of your trade.
Margin explained
Leveraged trading is also known as ‘trading on margin,’ because the funds required to open and maintain a position – the ‘margin,’ are only a fraction of the total amount.
When trading CFDs, you have two options for margin. A deposit margin is required to open a position, and a maintenance margin may be required if your trade is about to lose money that the deposit margin – and any extra funds in your account – cannot cover. If this happens, your provider may contact you and ask you to add funds to your account. The deal will be canceled and any losses will be recognized if you do not add enough money to the account.
Margin and leverage are closely related terms that are sometimes misunderstood or wrongly used interchangeably.
Leverage needs margin. A margin deposit is required for an account. This margin is used to multiply position sizing as collateral.
All CFD trading accounts should assign adequate margin to cover all trades, as well as additional margin to protect against liquidation if a deal goes against them.
Larger position sizes or a greater number of positions necessitate more margin. A margin call will be issued as a warning if not enough margin is held. Then, to cover the total margin required to settle all open positions, all open positions will be liquidated. Any remaining margin will be credited back to a user’s trading account.
Hedging
Hedging is best understood as a type of insurance. When people decide to hedge, they are protecting themselves from the financial consequences of a negative incident. This does not guarantee that all negative events will not occur. However, if a negative event occurs and you’ve appropriately hedged your bets, the impact of the occurrence is minimized.
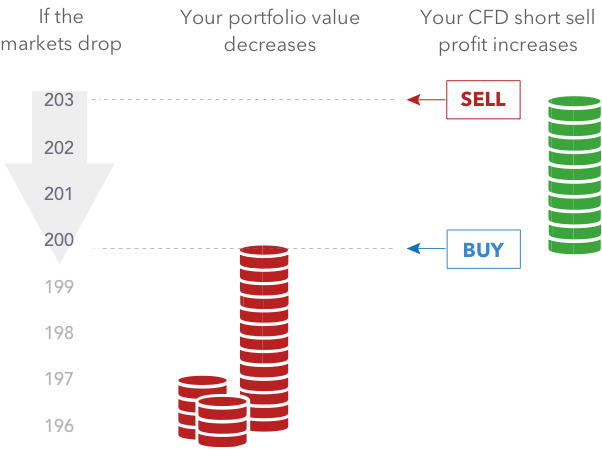
CFDs can also be used to protect a current portfolio from losses.
For example, if you anticipated that some ABC Limited shares in your portfolio may see a short-term drop in value as a result of a poor earnings report, you could mitigate some of the potential loss by selling short on the market via a CFD trade. Any loss in the value of the ABC Limited shares in your portfolio would be offset by a gain in your short CFD transaction if you decided to hedge your risk in this way.
How does CFD trading work?
Brokers produce a popular sort of derivative, take an underlying market, and create a new trading instrument in CFD trading. This new trading instrument is not constrained by the same regulations as a spot trading exchange, which allows traders to only purchase or sell assets that they already hold.
Because CFD trading is based on derivatives, it allows for the creation of new and even unusual trading products. CFDs can be traded in a variety of ways, but the most common ones are forex, stocks, stock indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
It’s time to look at how contracts for difference function now that you know what they are. Spreads, deal sizes, durations, and profit/loss are four of the most important principles in CFD trading.
Spread and commission
CFD pricing is broken down into two categories: buy and sell.
- The sell price (sometimes known as the bid price) is the price at which a short CFD can be opened.
- The buy price (or offer price) is the cost of opening a long CFD position.
Buy prices will always be somewhat higher than the current market price, and sell prices will always be slightly lower than the current market price. The spread refers to the difference between the two prices.
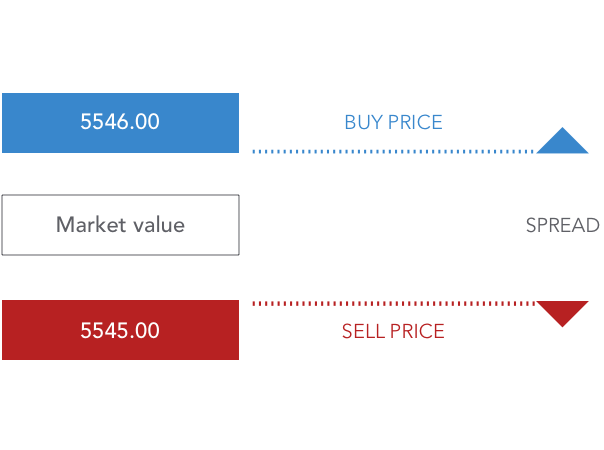
The cost of opening a CFD position is usually covered by the spread, which means that the buy and sell prices will be changed to reflect the cost of initiating the trade.
Deal size
CFDs are traded using standardized contracts. A single contract’s size varies depending on the underlying asset being traded and is typically modeled after how that asset is exchanged on the open market.
On the commodities markets, silver, for example, is sold in lots of 5000 troy ounces, and its equivalent contract for difference has a value of 5000 troy ounces as well. For share CFDs, the contract size is usually one share of the company you’re trading. To begin a position that simulated buying 500 HSBC shares, you would purchase 500 HSBC CFD contracts.
CFD trading also differs from other derivatives such as options in that it is more similar to regular trading.
Profit and loss
To determine the profit or loss from a CFD trade, multiply the position’s deal size (total number of contracts) by the contract’s value (expressed per point of movement). The difference in points between the price when you opened the contract and the price when you closed it is then multiplied by that figure.
Profit or loss = (no. of contracts x value of each contract) x (closing price – opening price)
Any charges or fees you pay would be subtracted from the total profit or loss from a trade. Overnight finance costs, commissions, and guaranteed stop fees are examples of these types of fees.
Let’s say you want to buy 50 FTSE 100 contracts at 7500.0 each. Each point of upward movement in the FTSE 100 is worth $500, whereas each point of downward movement is worth $500 (50 contracts multiplied by $10).
If you sell when the FTSE 100 is trading at 7505.0, your profit would be $2500
2500 = (50 x 10) x (7505.0 – 7500.0)
If you sell when the FTSE 100 is trading at 7497.0, your loss would be $150 -1500 = (50×10) x (7497.0 – 7500.0)
What is a CFD account?
A contract for difference (CFD) account allows you to leverage trade on the price difference between several underlying assets. Leverage refers to the fact that you only put up a portion of the money required to trade. This is referred to as a deposit margin. You’ll also need enough money in your account to cover any potential losses if your transactions go wrong. This is referred to as the “maintenance margin.”
Before your broker can give you margin trading, they need to know a little bit about you, so they require you to open a separate account and prove your identification and ability to cover losses. You can usually practice trading on a demo account, but you’ll need to deposit money into a CFD trading account before you can trade fully.
New customers must pass a ‘appropriateness’ test, which is mandated by some agencies. This usually entails answering a few questions to show that you’re aware of the heightened hazards – not simply the potential benefits – of trading on margin. Before trading, it’s best to learn everything there is to know about leverage and margin.
Some seasoned traders open multiple CFD accounts with the same broker to trade different assets or pursue different trading methods.
You may register on a reputable site, make a deposit, and go from position to profit in a short amount of time and with only a few simple actions:
Step 1: Open a CFD trading account
Before trading on a live account, traders can sign up on a platform of a CFD broker that offers demo accounts. PrimeXBT is a margin trading platform that provides an option to trade in a risk-free environment before trading with real funds. Traders can participate in Contests using demo funds to trade CFDs on a wide range of financial markets, including FX, Commodities, Stock indices, and Cryptocurrency assets.
Registration is quick and fast, takes less than a minute, and includes a trading account with multiple popular Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum and more. Your trading account balance is secured with bank-grade security and other safeguards including two-factor authentication and mandatory address whitelisting.
Step 2: Make your first deposit
To get started, PrimeXBT doesn’t require a minimum deposit, allowing you to choose the amount and currency you feel comfortable with. Funding your account is a crucial step that brings you closer to trading markets.
It’s critical to not only be comfortable with your first deposit, but to also ensure that your deposit is enough to prevent a margin call or a negative account balance. Negative balance protection is available on several systems. Depending on the predicted transaction volume, you’ll also want extra funds.
Keep in mind that most CFD brokers charge a commission on each trade, and some even charge a financing or funding cost to keep CFD positions open with collateral.
Step 3: Develop a trading strategy
Developing a trading strategy that consistently produces profits is far more difficult than it appears; yet, with time, talent, practice, and knowledge, it is feasible. Of course, luck can also play a role.
Technical analysis is critical to determining a buy price at which to enter and a sell price at which to exit.
It’s time to take a stand once you’ve devised a strategy.
Step 4: Take your position
Enter your target entry price to prepare for the position you wish to take. If the price is near, try using a market order to enter the transaction right away. If not, select a limit or stop order and submit your request.
After the order has been filled, set a stop loss and proceed to the next stage.
Step 5: Take your profit
All that’s left is to take profit after a desirable level or objective is reached, unless your stop loss is triggered before then.
Profiting frequently and even early is suggested. If the market turns around, you’ll be able to close the deal in profit rather than at a loss.
What assets can you trade with CFDs?
Many assets and securities, including exchange-traded funds (ETFs), can be exchanged through contracts for differences. Traders will also utilize these products to bet on price movements in commodity futures contracts, such as crude oil and corn futures.
Futures contracts are standardized agreements or contracts that require the buyer or seller to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price on a specific date in the future.
CFDs are not futures contracts in and of themselves, but they do allow investors to trade the price movements of futures. CFDs do not have predetermined prices or expiration dates, but they do trade like other securities with buy and sell prices. CFDs can be traded in a variety of ways, but the most prevalent are forex, stocks, stock indices, commodities, and cryptocurrencies.
How much should you invest?
CFD trading democratizes markets by lowering the entrance barrier. CFD trading is seen as a low-cost option to access the financial markets. CFD fees may include a commission for trading various financial assets with some brokers.
The spread – the gap between the buy and sell prices at the time you trade – is the most significant CFD fee. If a deal is held open overnight, there is an additional charge of an overnight fee.
Because CFDs are leveraged products, you can build considerably larger positions with a smaller initial investment than you would with ordinary shares.
CFD trading strategies
Day trading and swing trading are the two most prevalent techniques to trade CFDs. Both strategies have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, which you’ll find here. Despite the variations, both types of trading approaches should use the same tools and risk management. These fundamental elements of trading should not alter.
- Before taking any position always analyse the market, use technical analysis or other tools to help you understand the current conditions.
- Begin slowly and gradually gain experience with this high-risk, high-reward derivative trading product.
- Look for a trading platform or CFD broker with a good track record, robust trading tools, and dependable security.
- Before deciding on a platform, decide which markets you wish to trade. It will make the choice a lot easier.
- Choose a site that offers a wide range of CFDs on a variety of marketplaces. You can begin by using one trading instrument and then go on to another.
- Make sure to utilise correct risk management tactics on a regular basis. Always have a stop loss in place. Take this into account when estimating possible loss and profit if you’re utilising leverage.
- Be cautious when using leverage. If you’re not careful or make a mistake, you could lose everything you own.
- Always preserve extra margin in your account in case a profitable opportunity arises or a trade goes against you. A margin call or liquidation will be avoided as a result.
- Experiment with various CFDs and asset markets. These contracts’ moderate flexibility provides some intriguing trading opportunities.
Example of a CFD trade
Contracts for difference let you bet on the price movement of assets in either direction. This means that you can benefit not only when the market rises in price (goes long), but also when it falls in price (goes short).
- You buy or ‘go long’ if you feel the market will rise.
- If you feel the market will fall, you sell or ‘go short’.
You choose the number of contracts you want to trade (buy or sell) when you create a CFD position, and your profit grows with each point the market moves in your favor.
Example of going Long
You believe Tesla’s stock will rise in value and want to take advantage of this chance by opening a long CFD position.
You invest $16,000 in 100 CFDs on Tesla shares at $160 a share. You get a $1,000 profit if Tesla rises to $170.
The following is a synopsis of what’s going on:
- 165 You begin your market research.
- 160 You notice a drop in the price and decide to open a transaction (Buy the CFDs).
- 170 When the price of your CFD rises, you close your deal (Sell the CFDs) and make a $10 profit.
Example of going Short
You believe the price of Tesla will fall, and you want to profit from this trend. You can profit from a declining market by opening a short CFD position (also known as short-selling).
Let’s say you decide to sell 100 Tesla CFDs at $170 per share, which then drops to $160 per share. You’ll have made a $1,000 profit, or $10 per share.
The following is a synopsis of what’s going on:
- 165 You begin your market research.
- 170 When the price of your CFD rises, you open a trade (Sell the CFDs) and make a $10 profit.
- 160 When the price drops, you opt to exit the deal (Buy the CFDs).
Why trade CFDs with PrimeXBT?
Trading CFDS on PrimeXBT is simple, and the award-winning platform includes all of the advanced trading tools that anyone needs to make the most of their CFD trading.
Traders can go long or short on more than 100 different trading instruments, including Bitcoin and other Cryptocurrencies, FX, Commodities, metals, Stock indexes, and more. Any trader, new or seasoned, may use the whole arsenal to get the job done and learn how to succeed. There’s also a company blog providing trading advice, instructions, and other resources to help novices get started.
Trading involves risk.
The Copy Trading module is available for individuals who can’t seem to get it right or simply need a pause to refocus. Rather than trading CFDs themselves, traders can use Copy Trading module to copy other more successful Strategy Providers, who are all ranked by profits on a global leaderboard.
What is CFD trading?
CFD trading, or Contract for Difference trading, allows you to speculate on the price movements of financial assets like stocks, commodities, and Forex without owning the underlying asset. You can profit from both rising and falling markets by trading the price difference between your entry and exit points.
How do CFD traders make money?
CFD traders make money by correctly predicting price movements of an asset. Profits are earned from the difference between the asset's price when the trade is opened and closed. Traders can also amplify their gains using leverage, though this increases the risk of losses.
What are the risks of CFD trading?
The main risks of CFD trading include leverage, which can amplify losses, market volatility, and potential account liquidation if margin requirements are not met. Proper risk management, such as using stop-loss orders and limiting leverage, can help minimize risks.
Is CFD trading good for beginners?
Yes, CFD trading can be suitable for beginners due to its simplicity and the ability to trade small positions. However, it's important for beginners to understand the risks associated with leverage and market volatility. Starting with a demo account is highly recommended
Is CFD trading safe?
CFD trading is safe when conducted on a reputable platform with robust security measures like PrimeXBT. However, safety also depends on how well traders manage risks, such as using stop-losses and avoiding over-leveraging
Which CFD markets can I trade on?
CFDs are available on a variety of markets, including:
Forex: Currency pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/JPY.
Commodities: Gold, oil, and natural gas.
Indices: S&P 500, NASDAQ, and FTSE 100.
Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and more
What is CFD leverage trading?
Leverage in CFD trading allows you to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. For example, with 1:100 leverage, you can trade $10,000 worth of an asset by depositing just $100. While this magnifies potential profits, it also increases the risk of losses.
Can I use CFDs for hedging?
Yes, CFDs are an effective tool for hedging. For example, if you own stocks and anticipate a short-term market decline, you can open a short CFD position to offset potential losses in your portfolio.
The content provided here is for informational purposes only. It is not intended as personal investment advice and does not constitute a solicitation or invitation to engage in any financial transactions, investments, or related activities. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future results.
The financial products offered by the Company are complex and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. These products may not be suitable for all investors. Before engaging, you should consider whether you understand how these leveraged products work and whether you can afford the high risk of losing your money.
The Company does not accept clients from the Restricted Jurisdictions as indicated in our website/ T&C. Some services or products may not be available in your jurisdiction.
The applicable legal entity and its respective products and services depend on the client’s country of residence and the entity with which the client has established a contractual relationship during registration.




